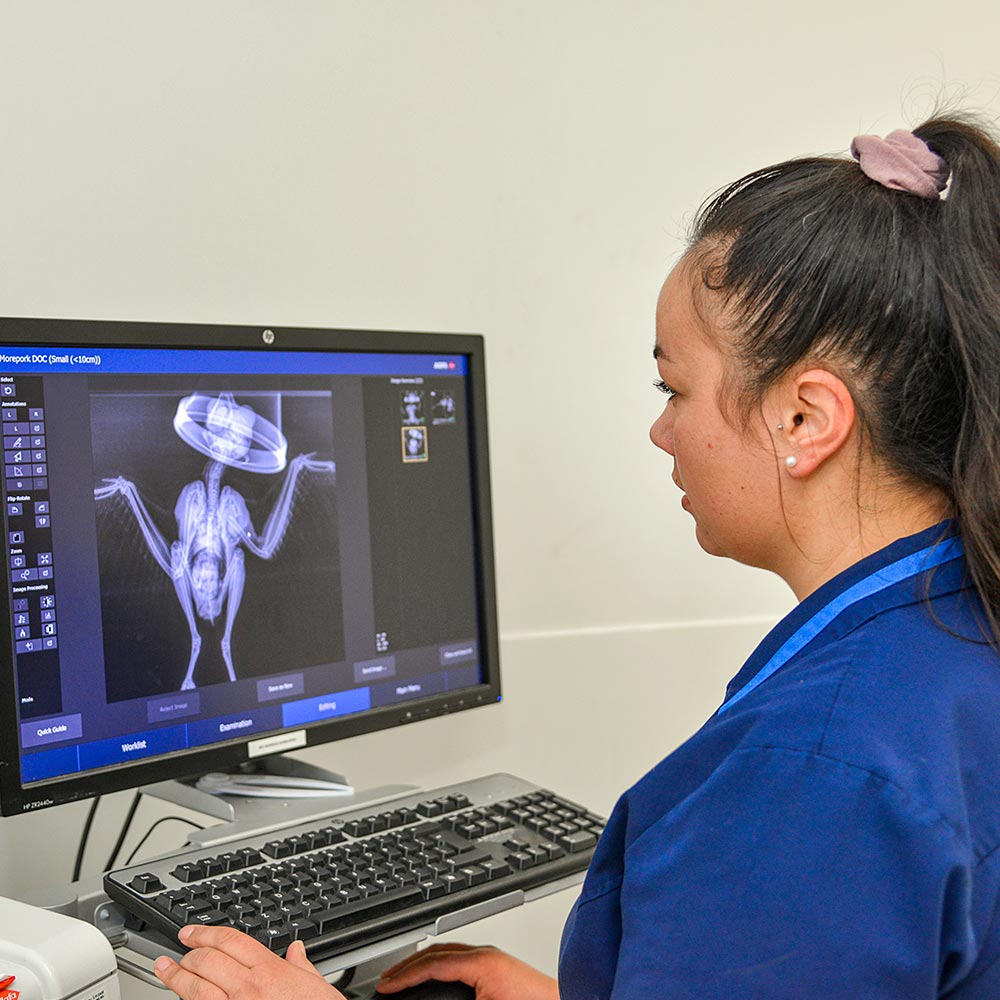
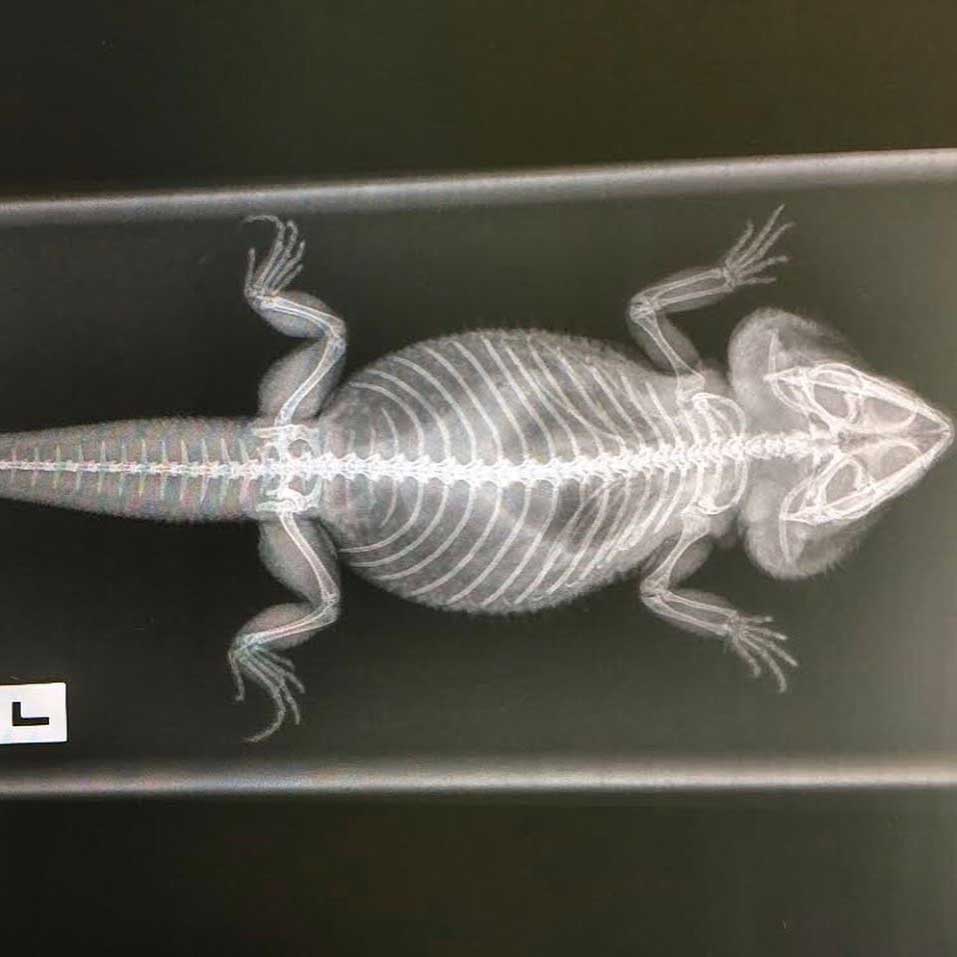
Our Pocket & Exotic Pet Services at a Quick Glance:
- 24/7 care with full after hours cover
- Surgical Services
- Artificial Insemination & Reproduction Management
- Pregnancy Scanning
- Vaccination Programmes
- Drench Resistance Programmes
- Disease Controls Plans
- Animal Health & Feed Planning
- Seminars and Staff Training